Understanding Heating in Vacuum Furnaces: The Core Principle
In a vacuum heat treatment furnace, heating methods determine how thermal energy is delivered to the workpieces. Since no oxygen is present, the process relies heavily on conduction, radiation, or induced currents, depending on the furnace design.
Practical Impact of Heating Methods
The heating method directly affects temperature control, uniformity, cycle time, energy consumption, and ultimately the quality of the treated components. Choosing the right method ensures stable metallurgical results and cost efficiency.
Why Aren’t All Heating Methods Universally Used?
Temperature Uniformity – Some methods provide more even heating, while others are prone to temperature gradients.
Energy Efficiency – High-efficiency heating may require more complex equipment.
Material Limitations – Certain alloys respond better to specific heating methods.
Equipment Complexity and Cost – Advanced systems like induction may cost more to build and maintain.
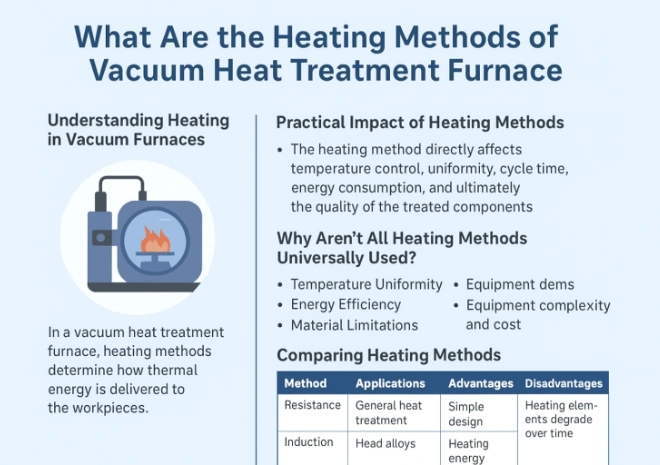
Comparing Heating Methods
Resistance Heating
Uses graphite or metal heating elements. Heat is transferred through radiation and conduction. Commonly used in most industrial vacuum furnaces.
Induction Heating
Generates eddy currents inside the material using electromagnetic fields, causing rapid and localized heating. Ideal for precision and high-speed applications.
Radiation Heating
Relies on high-temperature elements emitting radiant energy that heats the workpieces. Particularly useful in high-vacuum environments where convection is absent.
Where Each Heating Method Excels
Resistance Heating → General-purpose applications such as hardening, tempering, and brazing.
Induction Heating → Surface hardening, localized treatment, and applications requiring fast heating cycles.
Radiation Heating → Processes requiring high temperatures and uniformity, such as sintering and diffusion bonding.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Heating Method
Resistance Heating
Advantages: Simple design, stable operation, widely applicable.
Disadvantages: Heating elements degrade over time, slower heating speed.
Induction Heating
Advantages: Fast heating, high efficiency, precise control, minimal distortion.
Disadvantages: Higher equipment cost, limited to conductive materials.
Radiation Heating
Advantages: Clean heating method, excellent temperature uniformity in vacuum, suitable for extreme conditions.
Disadvantages: Lower heating speed, depends heavily on furnace design.
The Bottom Line
Heating methods in vacuum furnaces each have unique strengths. Resistance heating is versatile and widely used, induction heating excels in speed and precision, while radiation heating ensures uniformity at extreme conditions. The right choice depends on the process requirements and material characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the main heating methods used in vacuum furnaces?
A: Resistance heating, induction heating, and radiation heating.
Q: Which heating method is most common?
A: Resistance heating is the most widely used due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Q: Why choose induction heating in vacuum furnaces?
A: It offers rapid, localized heating with high energy efficiency, especially for surface treatments.
Q: What are the advantages of radiation heating?
A: It provides excellent uniformity and is effective under high vacuum and high temperature.
Q: Are all heating methods suitable for every material?
A: No, induction requires conductive materials, while resistance and radiation heating are more universal.
Q: Which industries prefer induction heating?
A: Aerospace, automotive, and tool manufacturing industries often use it for precision surface hardening








