How Vacuum Furnaces Work for Metal Processing?
1.Introduction to Vacuum Purification of Precious Metals
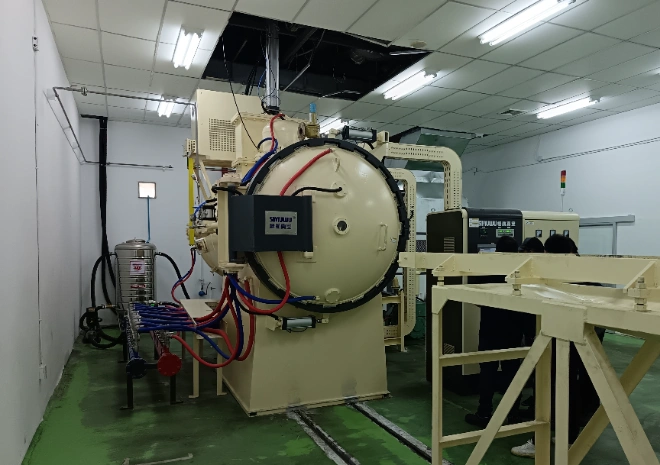

Precious metals, including gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, are valued for their rarity, durability, and unique properties. Purification is essential to remove impurities and achieve the high purity levels required for various industrial and commercial applications. Vacuum purification is a highly effective method for refining precious metals, offering advantages such as reduced oxidation, precise temperature control, and enhanced separation of volatile impurities。
2.Understanding the Science Behind Vacuum Purification
Boiling Point Reduction in Low-Pressure Environments
In a vacuum, the boiling point of substances decreases significantly due to the reduced atmospheric pressure. This allows precious metals to be heated to their boiling points at lower temperatures, minimizing thermal degradation and energy consumption。
Separation of Impurities Through Vaporization
Impurities with lower boiling points than the precious metal will vaporize first. By carefully controlling the temperature and pressure, these impurities can be separated and removed, leaving behind a higher-purity metal。
3.Key Components of a Vacuum Purification System
Vacuum Chamber and Pump
The vacuum chamber is a sealed environment where the purification process occurs. A vacuum pump removes air and gases from the chamber, creating the low-pressure conditions necessary for purification。
Heating System
An electric or induction heating system raises the temperature of the precious metal to its boiling point. Precise temperature control is crucial to ensure efficient evaporation and prevent overheating。
Condensation and Collection Units
As the purified metal vaporizes, it travels to a condensation unit where it cools and reverts to a solid state. The condensed metal is then collected for further processing or use。
4.Step-by-Step Guide to Vacuum Purifying Precious Metals
Preparation of Raw Materials
The raw precious metal, often in the form of scrap or alloy, is cleaned and prepared for purification. This may involve removing surface contaminants or breaking down larger pieces into smaller, more manageable sizes。
Loading the Vacuum Chamber
The prepared metal is placed inside the vacuum chamber. The chamber is then sealed to prevent air from entering during the purification process。
Establishing Vacuum Conditions
The vacuum pump is activated to remove air and gases from the chamber. A pressure control system maintains the desired vacuum level throughout the process。
Controlled Heating and Evaporation
The heating system raises the temperature of the metal to its boiling point. The rate of heating is carefully controlled to ensure uniform evaporation and prevent thermal shock。
Condensation and Recovery of Pure Metal
The vaporized metal travels to the condensation unit, where it cools and solidifies. The purified metal is then collected and stored for further use。
5.Advantages of Vacuum Purification Over Other Methods
Enhanced Purity Levels
Vacuum purification can achieve purity levels exceeding 99.99%, making it ideal for applications requiring ultra-pure metals。
Prevention of Oxidation
The absence of oxygen in the vacuum environment prevents oxidation, which can degrade the quality of the precious metal。
Reduced Energy Consumption
Lower boiling points in a vacuum reduce the energy required for purification, making the process more cost-effective and environmentally friendly。
6.Challenges and Considerations in Vacuum Purification
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Vacuum purification systems are complex and expensive to purchase and maintain. They require specialized knowledge to operate effectively。
Technical Expertise Required
Operators must have a deep understanding of vacuum technology, temperature control, and metal purification principles to ensure successful outcomes。
Handling and Safety Protocols
Precious metals and their vapors can be hazardous if not handled properly. Strict safety protocols must be followed to protect workers and the environment。
7.Applications of Vacuum-Purified Precious Metals
Jewelry and Artistic Applications
High-purity precious metals are essential for creating fine jewelry and artistic pieces, where quality and appearance are paramount。
Electronics and Semiconductor Industries
Ultra-pure metals are used in electronics and semiconductors, where even trace impurities can affect performance and reliability。
Medical and Dental Implants
Vacuum-purified metals are used in medical and dental implants due to their biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion。
8.Future Trends in Vacuum Purification Technology
Advancements in vacuum technology, materials science, and process control are expected to further improve the efficiency and effectiveness of precious metal purification. Innovations such as smart sensors, automation, and sustainable energy sources will drive the future of this field。
9.Summary
Vacuum purification is a highly effective method for refining precious metals, offering advantages such as enhanced purity, reduced oxidation, and lower energy consumption. While the process requires specialized equipment and expertise, its benefits make it a valuable tool in various industries.
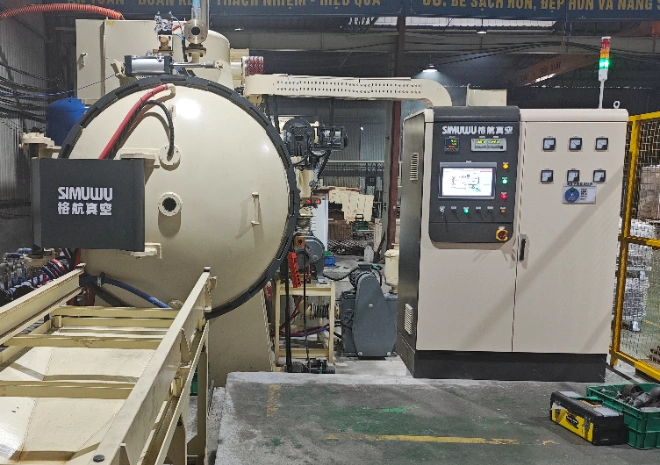

10.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the primary principle behind vacuum purification of precious metals?
A: The primary principle is reducing the boiling point of metals in a low-pressure environment, allowing impurities to be separated through controlled evaporation and condensation。
Q: What are the key components of a vacuum purification system?
A: The key components include a vacuum chamber, vacuum pump, heating system, and condensation/collection units。
Q: How does vacuum purification compare to chemical purification methods?
A: Vacuum purification is more environmentally friendly, as it generates minimal waste and emissions. It also achieves higher purity levels and prevents oxidation。
Q: What are the main challenges associated with vacuum purification?
A: The main challenges include the high cost and complexity of equipment, the need for technical expertise, and strict safety protocols。
Q: In which industries is vacuum-purified precious metal most commonly used?
A: Vacuum-purified precious metals are commonly used in jewelry, electronics, semiconductors, and medical industries。
Q: What are the advantages of using vacuum-purified precious metals in electronics?
A: Vacuum-purified metals offer high purity, which is crucial for electronics, where even trace impurities can affect performance and reliability。
Q: Can vacuum purification be used for all types of precious metals?
A: Yes, vacuum purification can be applied to various precious metals, including gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, as long as the process is tailored to the specific properties of each metal。
Q: What is the role of temperature control in vacuum purification?
A: Precise temperature control is essential to ensure uniform evaporation of the precious metal, prevent thermal shock, and achieve high purity levels。
Q: How does vacuum purification prevent oxidation during the refining process?
A: The absence of oxygen in the vacuum environment prevents oxidation, which can degrade the quality of the precious metal。
Q: What are the potential drawbacks of vacuum purification compared to other methods?
A: Potential drawbacks include the high cost of equipment, the need for specialized knowledge, and the complexity of the purification process。